Table of Contents
Skin So Bright: Understanding the Link Between Hyperpigmentation and Sun Exposure
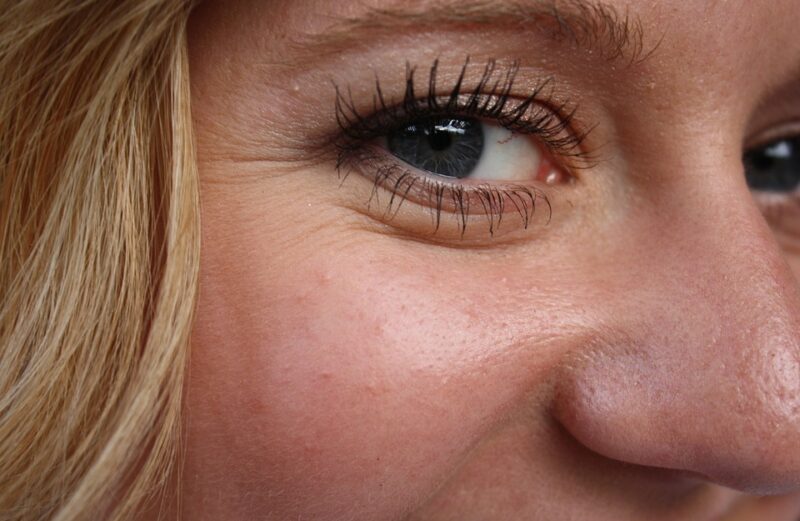
As the sun shines bright, we can’t help but want to bask in its warm glow. However, excessive sun exposure can have devastating effects on our skin, particularly in the long run. One of the most common consequences of chronic sun exposure is hyperpigmentation, a condition characterized by an excessive production of melanin, leading to darkened patches on the skin. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of hyperpigmentation, exploring its link to sun exposure, and offer practical tips to mitigate its effects.
The Science Behind Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is a result of an abnormal increase in melanin production, caused by various factors, including hormonal changes, inflammation, and environmental triggers. The process begins when the skin’s melanocytes, responsible for producing melanin, receive a signal to produce more melanin to protect the skin from harm. In response, they release excessive amounts of melanin, resulting in darkened patches or discoloration.
The Link Between Hyperpigmentation and Sun Exposure
Prolonged sun exposure is a primary contributor to hyperpigmentation. UV rays from the sun and tanning beds stimulate the melanocytes, triggering them to produce more melanin as a protective mechanism. This leads to the formation of darkened spots, often seen on the face, arms, and legs. Frequent exposure to the sun without adequate protection can exacerbate this condition, especially in individuals with darker skin tones, as their skin is naturally more susceptible to hyperpigmentation.
Tips for Reducing the Risk of Hyperpigmentation
Preventing hyperpigmentation is crucial to maintaining healthy, radiant skin. Here are some effective ways to minimize the risk of developing hyperpigmentation due to sun exposure:
• Practice Sun Safety: Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least 30, at least 30 minutes before heading outdoors. Reapply every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating.
• Wear Protective Clothing: Cover up with clothing that provides adequate UV protection, including wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts, and pants.
• Seek Shade: Whenever possible, stay in the shade, especially during peak sun hours (10am-4pm).
• Avoid Tanning Beds: Refrain from using tanning beds and artificial tanning devices, as they also emit harmful UV rays.
Additional Treatment Options for Existing Hyperpigmentation
If you’re already dealing with hyperpigmentation, there are various treatment options available to help alleviate the condition. Consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your specific skin type and concerns.
• Topical Creams: Prescription-strength creams containing hydroquinone, kojic acid, or retinoids can help reduce melanin production and even out skin tone.
• Chemical Peels: Gently exfoliating the skin with alpha-hydroxy acids or beta-hydroxy acids can help reduce hyperpigmentation by promoting cell turnover.
• Microdermabrasion: Non-invasive, non-ablative treatments can help remove the outermost layer of the skin, reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
By understanding the link between hyperpigmentation and sun exposure, we can take proactive measures to safeguard our skin from the devastating effects of excessive sun exposure. By adopting sun-safe habits and exploring treatment options, we can achieve healthier, more radiant skin.
Recommended Products
-
 Anua Peach 70 Niacin Serum 30mlKD8.000
Anua Peach 70 Niacin Serum 30mlKD8.000 -
 RDL Kalamansi Whitening Soap – 135gKD1.250
RDL Kalamansi Whitening Soap – 135gKD1.250 -
 Honest Glow Niacinamide Soap by Transformed Skin 100gKD2.500
Honest Glow Niacinamide Soap by Transformed Skin 100gKD2.500 -
 The Ordinary Azelaic Acid Suspension 10%KD6.000 – KD12.000
The Ordinary Azelaic Acid Suspension 10%KD6.000 – KD12.000 -
 ABCAQUIN 4% Hydroquinone Whitening & lightening Cream 30gKD4.000
ABCAQUIN 4% Hydroquinone Whitening & lightening Cream 30gKD4.000 -
 Honest Glow Glass Skin Soap – 80gKD2.500
Honest Glow Glass Skin Soap – 80gKD2.500 -
Product on sale
 Some By Mi AHA BHA PHA 30 Days Miracle Cream – 60gOriginal price was: KD10.000.KD8.000Current price is: KD8.000.
Some By Mi AHA BHA PHA 30 Days Miracle Cream – 60gOriginal price was: KD10.000.KD8.000Current price is: KD8.000. -
 The Ordinary Glycolic Acid 7% Exfoliating TonerKD6.000 – KD9.000
The Ordinary Glycolic Acid 7% Exfoliating TonerKD6.000 – KD9.000 -
Product on sale
 COSRX The Niacinamide 15 Serum – 20mlOriginal price was: KD11.990.KD10.000Current price is: KD10.000.
COSRX The Niacinamide 15 Serum – 20mlOriginal price was: KD11.990.KD10.000Current price is: KD10.000.





